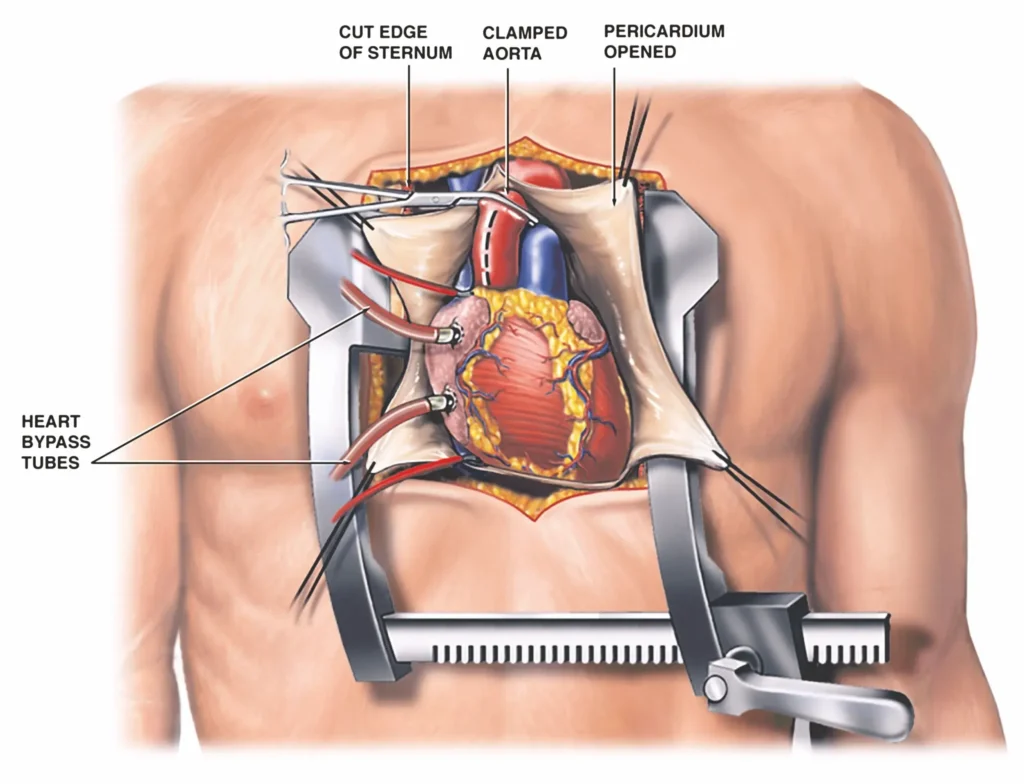
Open heart surgery is a procedure where the chest is opened to repair issues with the heart’s muscles, valves, or arteries. It is typically used for serious conditions such as blocked arteries, heart valve problems, and congenital heart defects.
Procedure
During open heart surgery, a heart-lung machine is used to take over the function of pumping blood and providing oxygen to the body while the surgeon works on the heart. This machine ensures that blood flow and oxygenation are maintained throughout the procedure.
Recovery
Recovery from open heart surgery generally takes several weeks. Patients must adhere to specific post-operative care instructions to promote healing and prevent complications. This includes following a prescribed medication regimen, attending follow-up appointments, and gradually resuming physical activity.
Advancements
Recent improvements in surgical techniques and post-operative care have significantly enhanced outcomes for patients undergoing open heart surgery. These advancements have contributed to better recovery rates and overall patient well-being.
In summary, open heart surgery is a critical procedure for addressing severe heart conditions, and ongoing advancements continue to improve its effectiveness and recovery process.
Symptoms
Severe chest pain (angina), Shortness of breath, Heart palpitations, Swelling in the legs, ankles, or feet (edema), Extreme fatigue, Unexplained weight gain (fluid retention)
Diagnosis
Treatment