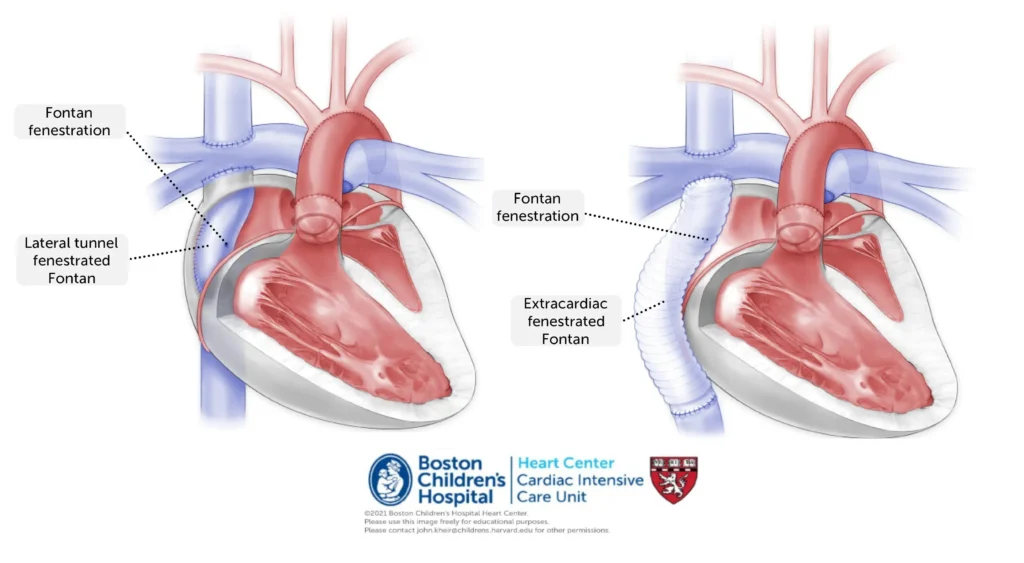
The Fontan procedure is a specialized surgery designed to address severe congenital heart defects, particularly for patients with only one functioning ventricle. Here’s an overview:
Purpose
Congenital Heart Defects (CHDs) are conditions present at birth that affect the heart’s ability to circulate blood effectively. The Fontan procedure is intended for individuals with a single effective heart chamber. It reroutes blood from a large vein in the lower body directly to the lungs, bypassing the heart to enhance blood flow and oxygenation.
Surgical Steps
Preoperative Planning: Detailed planning is essential before the surgery.
Anesthesia: General anesthesia is administered to ensure the patient is asleep during the procedure.
Bypass Creation: A graft is used to create a bypass, rerouting blood flow.
Monitoring: Postoperative care involves close monitoring to ensure recovery.
Postoperative Care and Benefits
Following the Fontan procedure, patients generally experience improved symptoms and a better quality of life, provided they adhere to regular follow-up visits to monitor heart function and overall health.
Future Directions
Advances in surgical techniques and research, including tissue healing and regeneration methods, are continually improving the outcomes of the Fontan procedure.
In summary, the Fontan procedure represents a significant advancement in the treatment of complex congenital heart conditions, reflecting ongoing progress in managing these challenging heart defects.
Symptoms
Diagnosis
Treatment